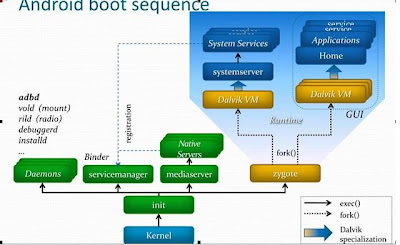
1. Boot Code (in Chip)
*Configure Chip: CPU, UART, Memory, (SD), Interrupt controller, watchdog, ...
*Download Boot Loader into Memory (Internal SRAM or external DRAM)
2. Boot Loader (e.g., U-boot)
*Initialize Source Sevice: NAND, SD, NOR, USB, Ethernet, ...
*Initialize Target memory: DRAM, ...
*Setup file system, network support, memory protections and security options, ...
*Download kernel & application images from source storage to target memory
3. Linux Kernel
*Set up interrupt controllers, MMU memory protections, caches and scheduling.
4. Android Init
4.1 Entry Point main() in ~/android/system/core/init/init.c
4.1.1 Clear the umask
4.1.2 Setup the basic filesystem (/dev, /proc, /sys)
4.1.3 Creates device nodes for kmsg and null (not /)
4.1.4 Initialize Log
4.1.5
Parse init.rc
4.1.6 Pull the kernel commandline and ramdisk properties file in
4.1.7 Parse hardware platform init.xxx.rc
4.1.8 Trigger "early-init"
4.1.9 device_init();
4.1.10 property_init();
4.1.11 Listen for keychords
4.1.12 Open console
4.1.13 Show "Android" by load_565rle_image(INIT_IMAGE_FILE)
4.1.14 property_set("ro.xxx", ...);
4.1.15 Trigger "init" (refer to init.rc)
4.1.16 start_property_service();
4.1.17 Create a signalling mechanism for the sigchld handler
4.1.18 Trigger "early-boot"
4.1.19 Trigger "boot" (refer to init.rc)
4.1.20 Run all property triggers
4.1.21 Register file descriptors with polling events
4.1.22 Infinite Loop
4.1.22.1 restart_processes() if needed
4.1.22 .2 Poll registered file descriptors
4.1.22 .3 Handle revents
4.2 Start Services in ~/android/system/core/rootdir/init.rc
*Services:
console, adbd,
servicemanager, vold, netd, debuggerd, ril-daemon, zygote, media, bootanim, dbus, bluetoothd, hfag, opush, pbap, installd, flash_recovery, racoon, mtpd, keystore, dumpstate
*See the following
root@android:/ # ps
USER PID PPID VSIZE RSS WCHAN PC NAME
root 1 0 296 204 c009b74c 0000caac S /init
root 2 0 0 0 c004e72c 00000000 S kthreadd
root 3 2 0 0 c003fdc8 00000000 S ksoftirqd/0
root 4 2 0 0 c004b2c4 00000000 S events/0
root 5 2 0 0 c004b2c4 00000000 S khelper
root 6 2 0 0 c004b2c4 00000000 S suspend
root 7 2 0 0 c004b2c4 00000000 S kblockd/0
root 8 2 0 0 c004b2c4 00000000 S cqueue
root 9 2 0 0 c018179c 00000000 S kseriod
root 10 2 0 0 c004b2c4 00000000 S kmmcd
root 11 2 0 0 c006fc74 00000000 S pdflush
root 12 2 0 0 c006fc74 00000000 S pdflush
root 13 2 0 0 c00744e4 00000000 S kswapd0
root 14 2 0 0 c004b2c4 00000000 S aio/0
root 22 2 0 0 c017ef48 00000000 S mtdblockd
root 23 2 0 0 c004b2c4 00000000 S kstriped
root 24 2 0 0 c004b2c4 00000000 S hid_compat
root 25 2 0 0 c004b2c4 00000000 S rpciod/0
root 26 1 728 404 c0025d68 afd0e56c S /system/bin/sh
system 27 1 836 264 c01a94a4 afd0dd3c S /system/bin/servicemanager
root 28 1 3760 528 ffffffff afd0e3ac S /system/bin/vold
root 29 1 3736 516 ffffffff afd0e3ac S /system/bin/netd
root 30 1 700 268 c01b52b4 afd0e6cc S /system/bin/debuggerd
radio 31 1 3356 656 ffffffff afd0e3ac S /system/bin/rild
nobody 32 1 63140 22560 00000000 8021c5f8 R zygote
media 33 1 19852 3724 ffffffff afd0dd3c S /system/bin/mediaserver
bluetooth 34 1 1288 600 c009b74c afd0eb7c S /system/bin/dbus-daemon
root 35 1 832 276 c01b52b4 afd0e6cc S /system/bin/installd
keystore 36 1 1644 404 c01b52b4 afd0e6cc S /system/bin/keystore
root 37 1 724 372 c0025d68 afd0e56c S /system/bin/sh
root 38 1 852 336 c00b8fec afd0eafc S /system/bin/qemud
root 40 1 1320 152 ffffffff 0000ee04 S /sbin/adbd
root 56 37 820 272 c02181f4 afd0da9c S /system/bin/qemu-props
root 64 26 924 348 00000000 afd0da9c R ps
*
kthreadd: Linex kernel thread daemon
4.3 Zygote: Start a Dalvik VM instance and System Server.
In ~/android/frameworks/base/cmds/app_process/app_main.cpp:
runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit",
startSystemServer);
In ~/android/frameworks/base/core/jni/AndroidRuntime.cpp:
void AndroidRuntime::start(const char* className, const bool startSystemServer)
if (startVm(&mJavaVM, &env) != 0)
In ~/android/frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/SystemServer.java:
startSystemServer(); 4.3.1 Dalvik VM
4.3.2 System Server: Add Critical System Services
In ~/android/frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/SystemServer.java
// Critical services...
try {
Slog.i(TAG, "Entropy Service");
ServiceManager.addService("entropy", new EntropyService());
Slog.i(TAG, "Power Manager");
power = new PowerManagerService();
ServiceManager.addService(Context.POWER_SERVICE, power);
Slog.i(TAG, "Activity Manager");
context = ActivityManagerService.main(factoryTest);
Slog.i(TAG, "Telephony Registry");
ServiceManager.addService("telephony.registry", new TelephonyRegistry(context));
AttributeCache.init(context);
Slog.i(TAG, "Package Manager");
pm = PackageManagerService.main(context,
factoryTest != SystemServer.FACTORY_TEST_OFF);
ActivityManagerService.setSystemProcess();
mContentResolver = context.getContentResolver();
// The AccountManager must come before the ContentService
try {
Slog.i(TAG, "Account Manager");
ServiceManager.addService(Context.ACCOUNT_SERVICE,
new AccountManagerService(context));
} catch (Throwable e) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Failure starting Account Manager", e);
}
Slog.i(TAG, "Content Manager");
ContentService.main(context,
factoryTest == SystemServer.FACTORY_TEST_LOW_LEVEL);
Slog.i(TAG, "System Content Providers");
ActivityManagerService.
installSystemProviders();
Slog.i(TAG, "Battery Service");
battery = new
BatteryService(context);
ServiceManager.addService("battery", battery);
Slog.i(TAG, "Lights Service");
lights = new
LightsService(context);
Slog.i(TAG, "Vibrator Service");
ServiceManager.addService("vibrator", new
VibratorService(context));
// only initialize the power service after we have started the
// lights service, content providers and the battery service.
power.init(context, lights, ActivityManagerService.getDefault(), battery);
Slog.i(TAG, "Alarm Manager");
AlarmManagerService alarm = new
AlarmManagerService(context);
ServiceManager.addService(Context.ALARM_SERVICE, alarm);
Slog.i(TAG, "Init Watchdog");
Watchdog.getInstance().init(context, battery, power, alarm,
ActivityManagerService.self());
// Sensor Service is needed by Window Manager, so this goes first
Slog.i(TAG, "Sensor Service");
ServiceManager.addService(Context.SENSOR_SERVICE, new
SensorService(context));
Slog.i(TAG, "Window Manager");
wm =
WindowManagerService.main(context, power,
factoryTest != SystemServer.FACTORY_TEST_LOW_LEVEL);
ServiceManager.addService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE, wm);
((ActivityManagerService)ServiceManager.getService("activity"))
.setWindowManager(wm);
5. Start-up Complete
*Broadcast ACTION_BOOT_COMPLETED
[]
http://hi.baidu.com/j_fo/blog/item/c782b11bbb16f1178618bf82.html
[]
The Android boot process from power on
[]
如何去寫Android init.rc (Android init language)
[]
http://source.android.com/porting/bring_up.html
[]
http://blog.chinaunix.net/u2/87328/showart_1678365.html
[] Android Zygote Startup